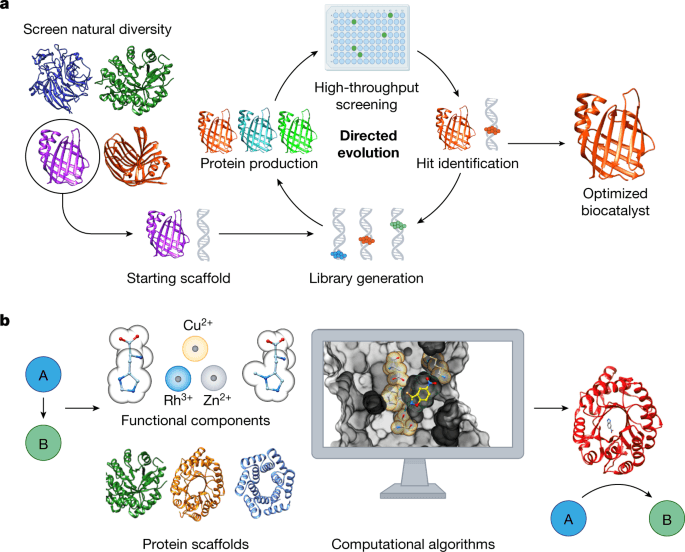
The time may come when we can use these techniques to program functionality into living organisms in the same way that we can program a computer to perform specific tasks. However, this is profoundly challenging because of the extreme complexity of living organisms. Editing an organism's DNA has direct effects on the proteins it synthesises, but we are not yet able to reliably and swiftly map genotypes to phenotypes — that is, the effects of this editing on its overall traits and behaviour are far more indirect and difficult to predict. Here, AI is expected to play a crucial role in enabling “rational design”.3
If harnessed to its full potential, synthetic biology could radically remake many industries and sectors of society. It may help mitigate climate change, for example, through engineering of organisms that pull CO2 from the atmosphere. It also has great potential to assist the move towards a circular bioeconomy, reducing the exploitation of natural resources and the associated harms to the Earth system through increasing emphasis on reuse and recycling of existing biological products.4
A key challenge for synthetic biologists is to create universal platforms on which research and development can be carried out.5 Such standardised systems — analogous to the operating systems of computers or the protocols which underpin the internet, and thus sometimes dubbed the “biotic internet” — will accelerate progress by making synthetic biology's tools much more accessible. The aim is to make synthetic biology a widespread and accepted cultural practice, just as computer coding has already become.
SELECTION OF GESDA BEST READS AND KEY REPORTS:
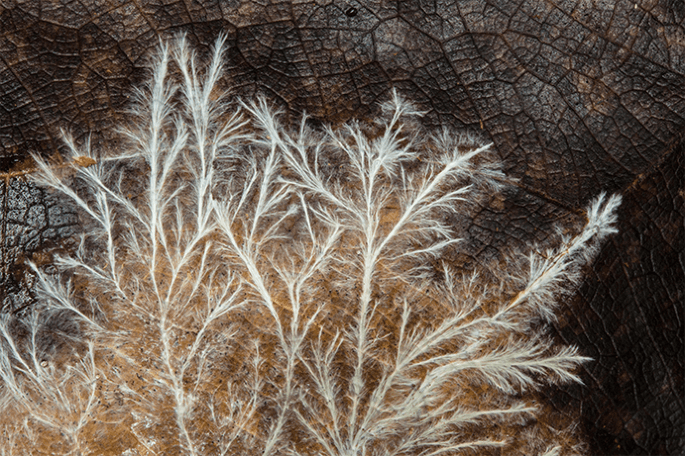
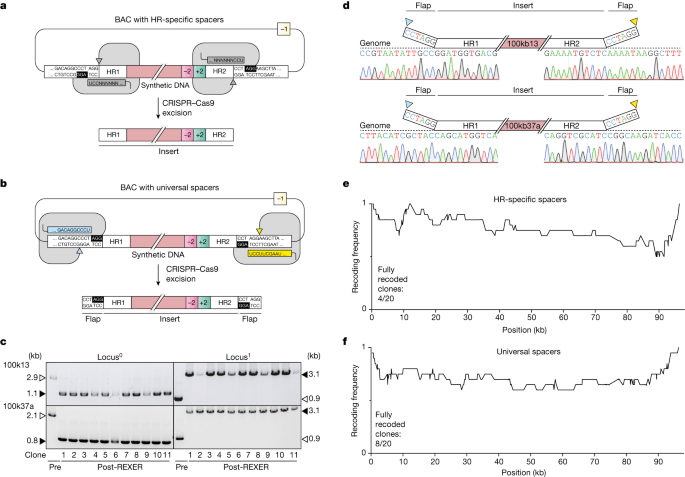
In June 2023, experts published on the innovative techniques that had allowed synthesis of entire E. coli genomes in a record time of under two months. Continuous synthesis of E. coli genome sections and Mb-scale human DNA assembly presented profound implications for genetic exploration and manipulation. In August, a research team in Australia and the US published Engineered bacteria detect tumor DNA, an innovative application of synthetic biology in devising cellular biosensors. These engineered Acinetobacter baylyi are adept at detecting DNA from colorectal tumors, proving instrumental both in vitro and in vivo, unveiling the potential of CRISPR-discriminated horizontal gene transfer as a revolutionary biodetection tool. Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules, presented by a research team from California in December, introduces a gamut of synthetic cell adhesion molecules. These custom-made molecules offer insights into cell-cell interfaces evolution and enable systematic cellular organisation and tissue modification.