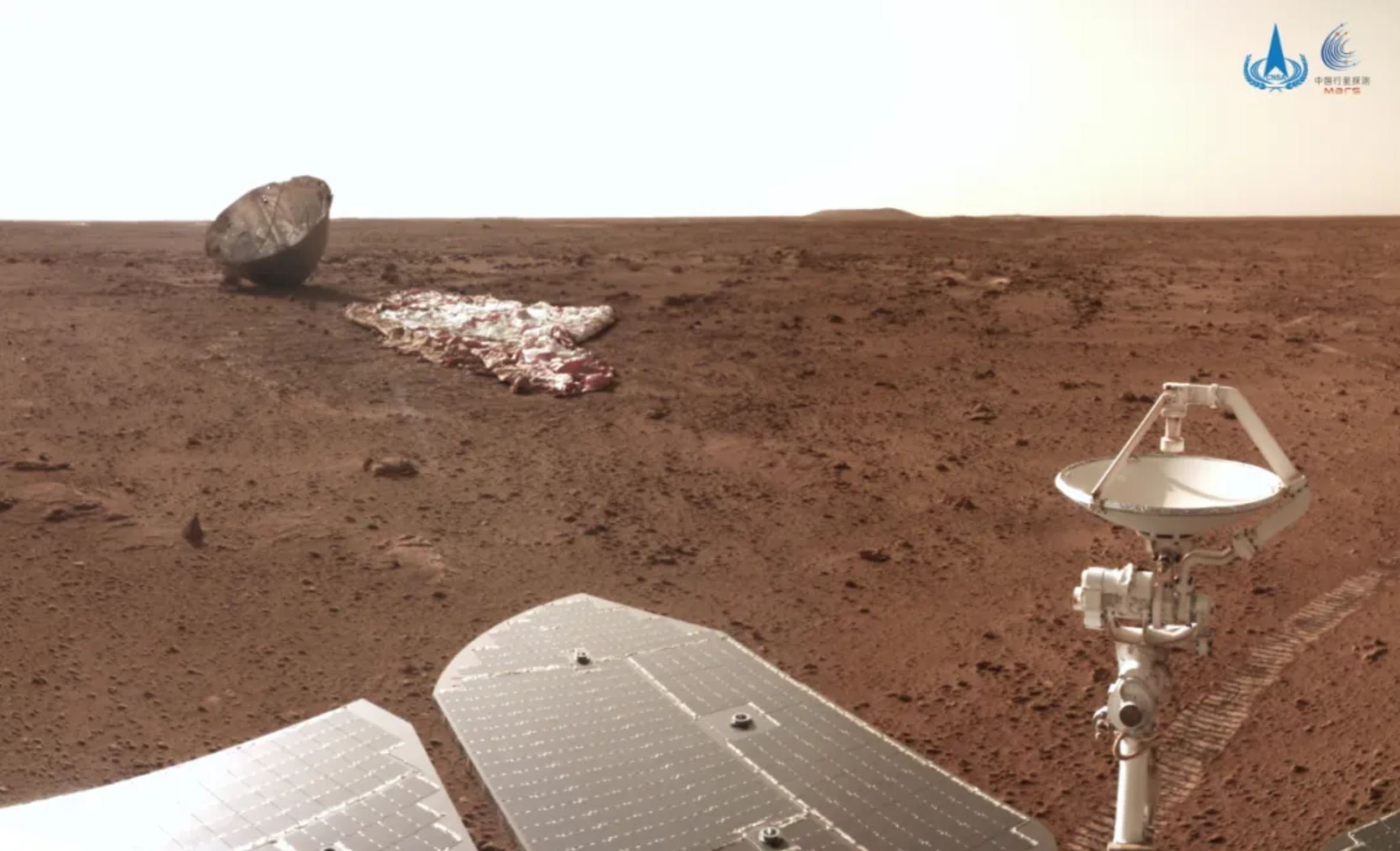
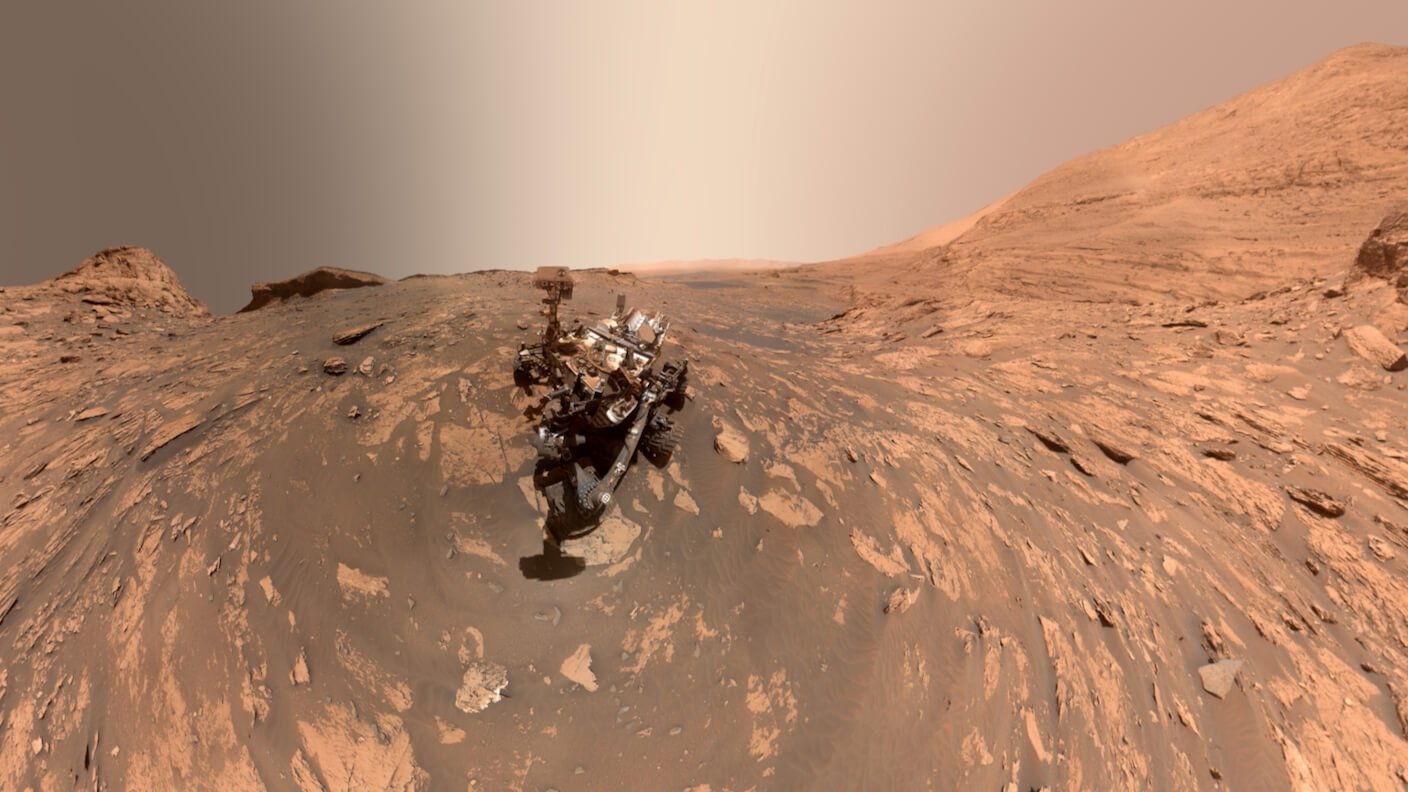
Since the first successful flyby in 1965, the space agencies that have successfully made it to Mars are: NASA, the former Soviet Union space program, the European Space Agency, the Indian Space Research Organisation, and most recently, the United Arab Emirates Space Agency and the China National Space Administration.47
A human presence on neighbouring planet Mars is an entry-level requirement to becoming a spacefaring society, an important step towards deepening our appreciation of our home planet Earth, and also a necessary one to avoid eventual extinction, whether from the expansion of the Sun or other extinction level events like a major asteroid impact that could potentially happen much sooner.
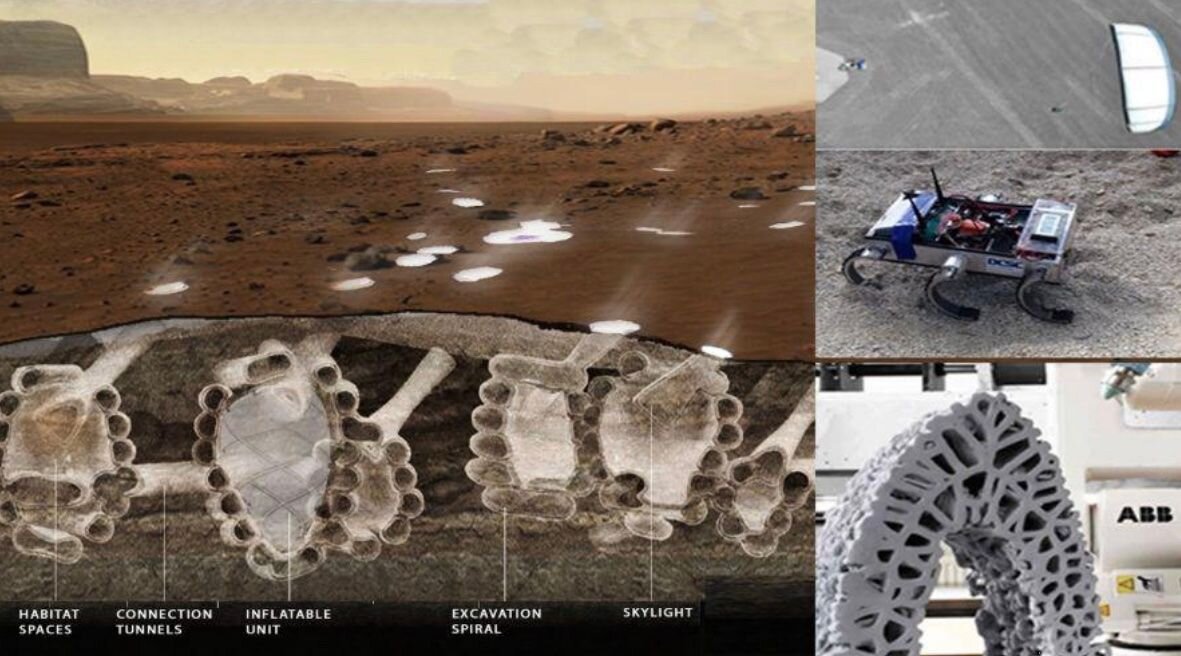
Two decades of human habitation of the International Space Station have led to impressive developments in the basic technological requirements for life beyond Earth: pressurised habitats; solar technology; water filtration systems; LED lighting to grow food; as well as communications systems, to name but a few. Thanks to detailed knowledge of conditions on the surface of Mars from over a half-century of remote exploration, we have far more detailed knowledge of what to expect there than early explorers had setting out to cross oceans, or even the Apollo astronauts when landing on the Moon.
Mars is more than 200 million km away on average, and in the absence of a foreseeable commercial angle for the time being, sending humans there could be considered humanity’s most aspirational endeavour. Human settlements on Mars are far enough away from Earth, on average 10 light minutes, to provide an opportunity to rethink the models of governance and economics on which our activities on Earth, and perhaps soon the Moon, are based.
In 2017, the United Arab Emirates announced a 100-year plan to build a city on Mars by 2117.48 The UAE’s first mission to Mars, the Hope orbital probe, is currently in orbit around the planet. SpaceX is on a slightly tighter schedule with founder Elon Musk’s aim of a city of one million on Mars by 2050.49 For that purpose, SpaceX is developing the Starship, a fully reusable transportation system designed to carry both crew and cargo to and from Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars and beyond. Starship is designed to be the most powerful launch vehicle developed by humanity so far, with the ability to carry in excess of 100 metric tons to Earth orbit, and around 100 people at a time to and from the surface of the Moon and Mars. The system could even be used for high-speed journeys between destinations on Earth, and eventually carry people to destinations beyond the asteroid belt.
SpaceX founder and CEO Elon Musk said that he's "highly confident" SpaceX will launch people toward the Red Planet in 2026,50 with the Starship ready for its first uncrewed mission to Mars in 2024.51
The US has been talking about sending crews to Mars for decades,52 now aiming for sometime in the 2030s,52 while China has recently announced plans to put humans on Mars by 2034.53